Electric motors and battery packs are just two of the parts that power EVs. Electric car’s main benefit is that they don’t emit any toxins, which is good for the environment.
Battery Pack
Electric vehicle battery (EVB) is another name for a traction battery pack. It provides electricity to an electric vehicle’s motors. The battery serves as a power storage system. It stores energy in the form of direct current (DC).
The range will increase when the battery’s kW increases. The design of the battery influences its life and functioning. A traction battery pack’s lifespan is expected to be 200,000 miles.
- A steady voltage is provided by the traction battery pack. However, various vehicle components have varied needs.
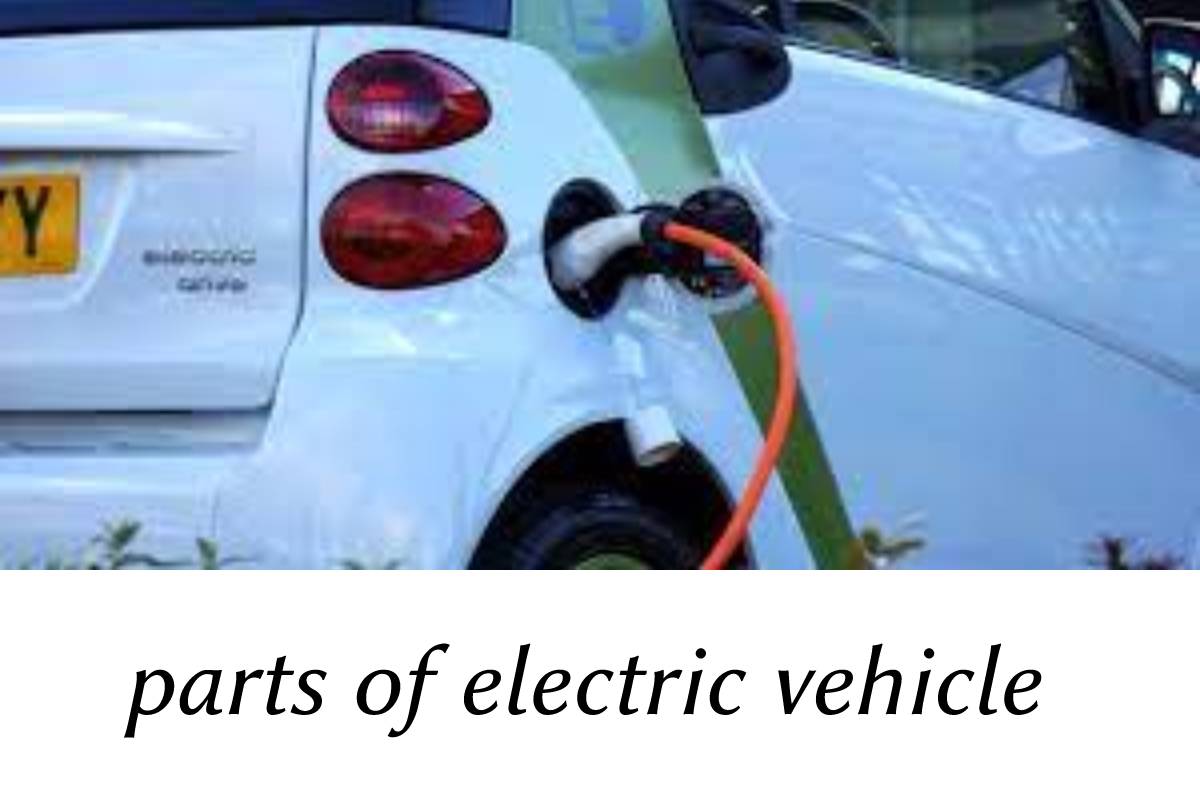
- Additionally, the charge port connects the electric vehicle to an external supply. It charges the battery pack.
- The charge port is sometimes located in the front or rear part of the vehicle.
- The onboard charger is used to convert the AC supply received from the charge port to a DC supply.
- The onboard charger is located and installed inside the car.
- It monitors various battery characteristics and controls the current flowing inside the battery pack.
- A power electronics controller determines the working of an electric car.
- It performs the regulation of electrical energy from the batteries to the electric motors.
- The pedal set by the driver determines the speed of the car and the frequency of variation of voltage that is input to the motor. It also controls the torque produced.
- Moreover, The essential component of an electric vehicle is the electric traction motor.
- The motor is responsible for converting electrical energy into kinetic energy. The wheels are rotated by this energy.
- The major component that distinguishes an electric automobile from a normal car is its electric motor.
- The regenerative braking system is a significant
- characteristic of an electric motor.
- To add, this system slows the vehicle down by transforming its kinetic energy into a different form and storing it for later use.
Parts of motors
There are two different parts of motors. They are DC motors and AC motors.
- It converts DC power from the batteries to alternating current electricity.
- It also transforms the alternating current generated from regenerative braking into a direct current.
- We also utilize this to recharge the batteries as well.
- The thermal management system is in charge of keeping the key components of an electric vehicle, such as the electric motor and controller, at a constant working temperature.
- It also maintains Optimal functionality while charging.
- Combining thermoelectric, forced air, and liquid cooling.
- The transfer of mechanical power from the electric motor to the wheels happens through a gearbox
- Electric vehicles have the benefit of not requiring multi-speed gearboxes. To minimize power loss, transmission efficiency should be good.
- Together, these cutting-edge materials enable automobile makers to design vehicles with greater range while meeting stringent safety criteria.


